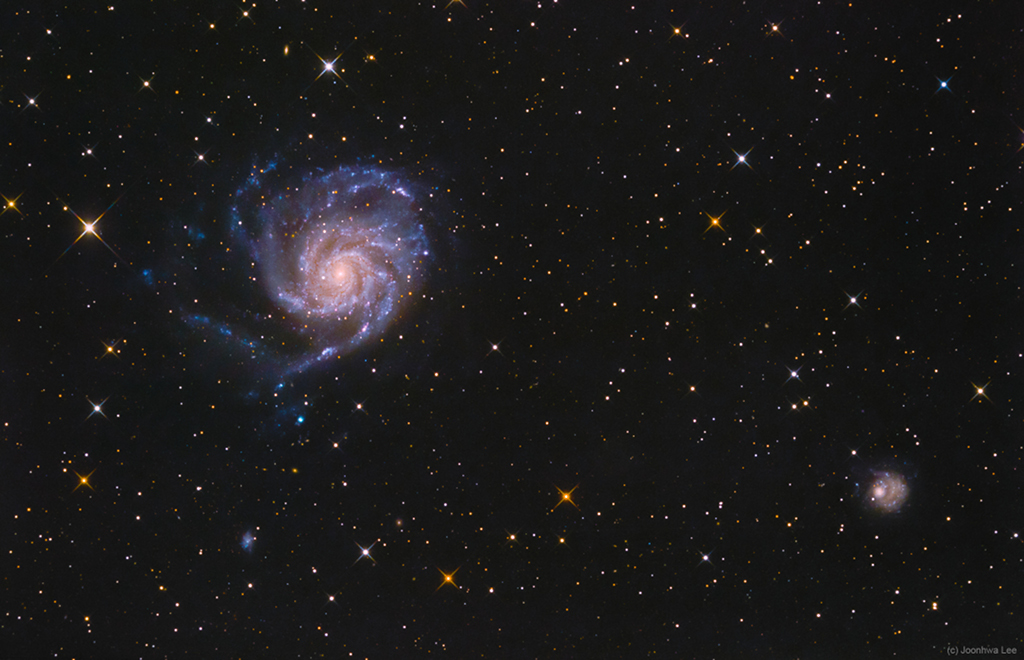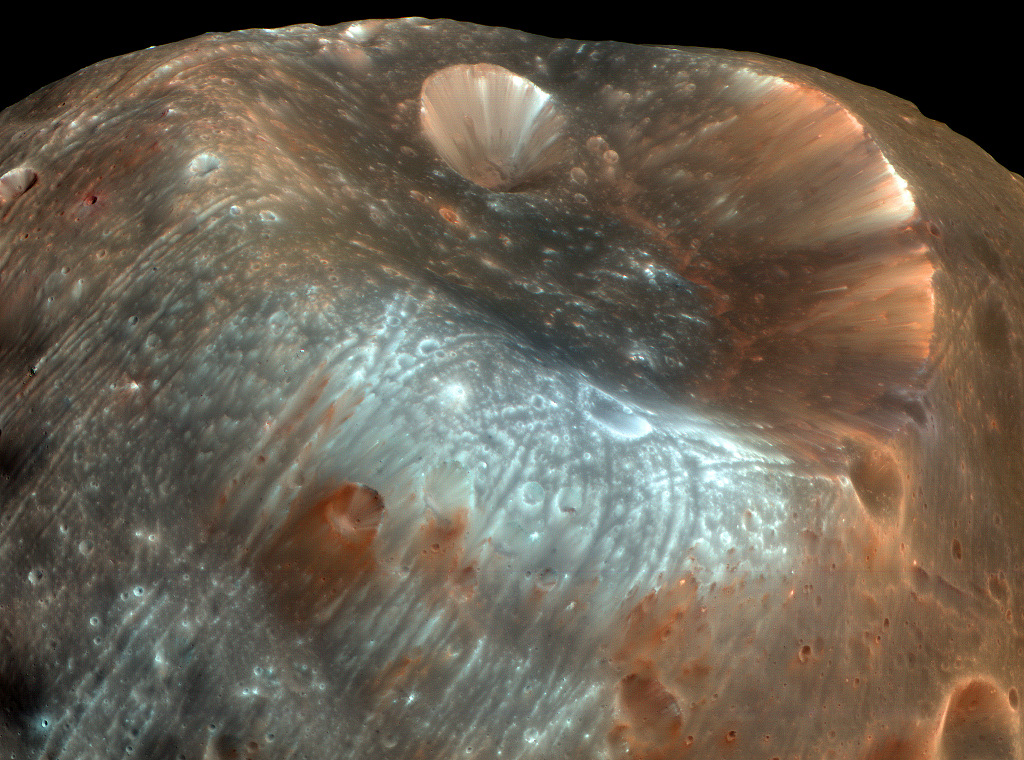
Stickney Crater, the largest crater on the martian moon Phobos, is named for Chloe Angeline Stickney Hall, mathematician and wife of astronomer Asaph Hall. Asaph Hall discovered both the Red Planet’s moons in 1877. Over 9 kilometers across, Stickney is nearly half the diameter of Phobos itself, so large that the impact that blasted out the crater likely came close to shattering the tiny moon. This stunning, enhanced-color image of Stickney and surroundings was recorded by the HiRISE camera onboard the Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter as it passed within some six thousand kilometers of Phobos in March of 2008. Even though the surface gravity of asteroid-like Phobos is less than 1/1000th Earth’s gravity, streaks suggest loose material slid down inside the crater walls over time. Light bluish regions near the crater’s rim could indicate a relatively freshly exposed surface. The origin of the curious grooves along the surface is mysterious but may be related to the crater-forming impact.
from NASA https://ift.tt/2rkUeNN
via IFTTT



