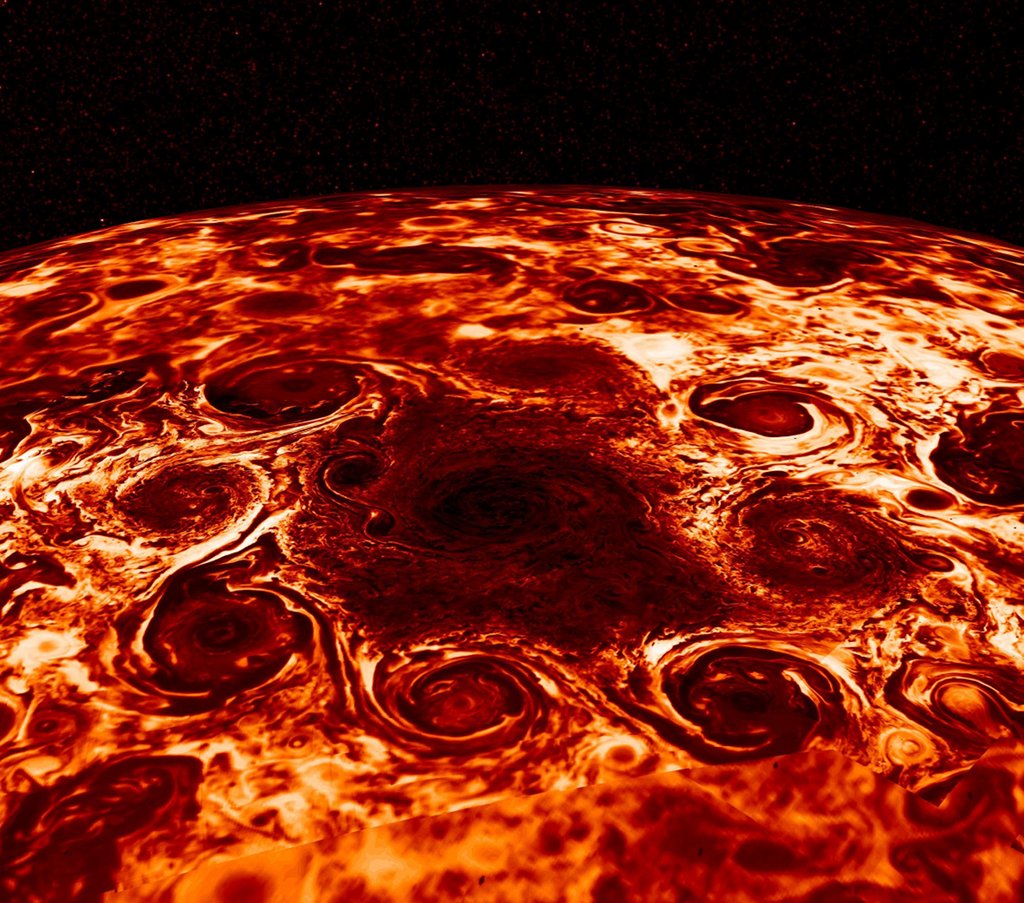
Juno’s Jovian Infrared Auroral Mapper data was used to construct this stunning view of cyclones at Jupiter’s North Pole. Measuring the thermal emission from Jovian cloud tops, the infrared the observations are not restricted to the hemisphere illuminated by sunlight. They reveal eight cyclonic features that surround a cyclone about 4,000 kilometers in diameter, just offset from the giant planet’s geographic North Pole. Similar data show a cyclone at the Jovian South Pole with five circumpolar cyclones. The South Pole cyclones are slightly larger than their northern cousins. Cassini data has shown that gas giant Saturn’s north and south poles each have a single cyclonic storm system.
from NASA http://ift.tt/2Fq3HIN
via IFTTT




